Sound Transmission Class (STC) Ratings for Flooring
Contents
- Introduction to Sound Transmission Class (STC)
- Flooring Acoustics: STC and IIC Ratings
- Understanding Sound Transmission
- STC Rating Scale
- Materials and Their STC Ratings
- Impact of STC on Building Design
- Enhancing STC Ratings in Flooring
- Case Studies
- Future Trends in STC Ratings
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the Sound Transmission Class (STC) rating for flooring?
- How is the STC rating determined for flooring?
- What factors can affect the STC rating of flooring?
- What STC rating is considered to be good for flooring?
- Can flooring with a high STC rating completely eliminate noise from transferring between spaces?
- Is the STC rating the only factor to consider when choosing flooring for noise reduction?
Introduction to Sound Transmission Class (STC)
 Knowing how sound moves through floors is important for building projects. The Sound Transmission Class (STC) rating measures sound reduction performance, helping you choose the right building materials for optimal acoustic comfort. In this article, we will discuss how STC ratings affect your design decisions, the different types of sound transmission you might face, and practical soundproofing methods to improve your space.
Knowing how sound moves through floors is important for building projects. The Sound Transmission Class (STC) rating measures sound reduction performance, helping you choose the right building materials for optimal acoustic comfort. In this article, we will discuss how STC ratings affect your design decisions, the different types of sound transmission you might face, and practical soundproofing methods to improve your space.
Key Takeaways:
Definition of STC
STC is defined as a single-number rating that indicates how well a building material attenuates sound, measured in decibels (dB).
This rating is derived from measurements at various frequencies, typically between 125 Hz and 4000 Hz, reflecting how materials resist sound transmission. Standards such as ASTM E90 guide these measurements, ensuring consistency and reliability.
For example, a wall with an STC rating of 50 will lower sound by roughly 50 dB, which makes it good for places that need to be quiet. Materials commonly tested include gypsum board, concrete, and resilient channels, each impacting the overall STC value based on thickness and density.
Importance of STC Ratings in Flooring
STC ratings are essential for flooring materials, as they directly influence privacy and noise control in both residential and commercial environments.
An STC rating typically ranges from 50 to 60 for effective sound reduction in multi-family dwellings, while a rating of 70 is recommended for high-end apartments or hotels.
Concrete slabs can reach an STC of 60, which makes them ideal for spots where reducing noise is important. In contrast, lightweight materials like vinyl might only reach 45.
Choosing the right flooring for your needs is important. For instance, a carpet with padding underneath can really help with soundproofing in a home.
Flooring Acoustics: STC and IIC Ratings
Flooring Acoustics: STC and IIC Ratings
Sound Transmission Class (STC) Ratings: Floor-Ceiling Structures
Sound Transmission Class (STC) Ratings: Drywall STC
Sound Transmission Class (STC) Ratings: Recommended STC Values
Impact Insulation Class (IIC) Ratings: Flooring Types
Impact Insulation Class (IIC) Ratings: Typical Laboratory IIC
The Flooring Acoustics data gives a useful view of how well various materials and building techniques work in blocking sound, concentrating on Sound Transmission Class (STC) and Impact Insulation Class (IIC) ratings. These measurements are important for designers and builders to make sure spaces have the right sound quality for their purpose.
Sound Transmission Class (STC) Ratings measure how effectively building components block airborne sound. Floor-Ceiling Structures in lightweight residential construction typically have an STC rating of 30.0, indicating minimal soundproofing suitable for less noise-sensitive areas. In contrast, 55.0 STC for commercial construction demonstrates a higher sound barrier, essential for office privacy and reduced external noise disturbances.
- Drywall STC ratings range from 33.0 for standard walls without insulation, highlighting the potential for noise leakage, to 39.0 when extra fiberglass insulation is added, providing better soundproofing.
- Recommended STC Values suggest 45.0 for effective privacy in residential settings, ensuring conversations remain confidential, while 60.0 is ideal for music rooms, providing a high level of acoustic isolation to prevent sound distortion and leakage.
Impact Insulation Class (IIC) Ratings assess how well floors reduce impact noise, such as footsteps. Flooring Types reveal that bare concrete slabs have a low IIC of 29.0, often unsuitable for residential applications due to significant noise transmission. In contrast, commercial construction with carpet achieves a higher IIC of 55.0, effectively minimizing impact sound and enhancing acoustic comfort.
- Typical Laboratory IIC results show engineered hardwood with underlayment at 54.5, providing a balance between aesthetics and impact noise reduction. Similarly, solid parquet with foam backing achieves an IIC of 55.0, demonstrating effective sound insulation in both practical and testing environments.
These Flooring Acoustics Ratings are important for places where sound control is needed, like homes, offices, and places like music studios. By knowing STC and IIC values, experts can choose the right materials and designs that meet sound requirements, providing the best sound settings for various purposes.
Understanding Sound Transmission

Grasping how sound travels is important for soundproofing, influencing design and material options.
Types of Sound Transmission
There are primarily two types of sound transmission to consider: airborne sound and impact sound, each influencing design strategies differently.
Airborne sound travels through the air, often resulting from conversations or music. This type is important in open office designs where noise can interrupt concentration.
To mitigate airborne sound, professionals often recommend using sound-absorbing materials like acoustic panels or carpets.
In contrast, impact sound occurs when objects hit a surface, such as footsteps on a floor. This is particularly relevant in multi-story apartments.
To manage impact noise, strategies like installing floating floors or using underlayment can be effective, enhancing overall soundproofing in shared spaces.
Factors Affecting Sound Transmission
Multiple factors contribute to the effectiveness of sound transmission reduction, including material type, thickness, and installation quality.
Picking the correct materials is important for soundproofing. For instance, mass-loaded vinyl (MLV) offers high-density soundproofing and works well when used in walls or ceilings. Using thicker drywall, such as 5/8 inch, greatly reduces sound.
To make sure insulation works well, seal it tightly and avoid leaving any spaces during installation. Using acoustic caulk can help seal edges and prevent sound leaks. Mixing these materials, customized for the area, can effectively reduce noise transmission.
STC Rating Scale
The STC rating scale gives a simple way to measure how well a material blocks sound. It ranges from low to high scores, helping you choose the right materials.
How STC Ratings are Measured
STC ratings are measured using controlled laboratory tests per ASTM E90 standards, assessing sound pressure levels across frequency bands.
To effectively measure STC ratings, you need a sound level meter calibrated to A-weighting standards and a controlled environment, such as a sound booth.
- Begin by sealing all gaps in the test structure.
- Next, set the meter at a specified distance (usually 1 meter) from either side of the wall or partition being tested.
Keep background noise steady to prevent distorted outcomes. After gathering data at different frequencies, use the results to determine the STC rating, offering important information about sound insulation effectiveness in various uses.
Interpreting STC Ratings
Knowing how to read STC ratings means knowing what the numbers mean for how well materials block sound.
An STC rating measures a material’s ability to block sound, with higher numbers signifying better sound insulation. For instance, a rating of 30 is typical for standard interior walls, while an STC of 50 or higher is ideal for noise-sensitive environments like recording studios.
Common materials include:
- drywall (STC 30-40)
- soundproofing foam (STC 35-50)
- concrete blocks (STC 50+)
When selecting materials, consider both application and environment, ensuring you match the STC needs-residential spaces often require lower ratings than commercial areas, particularly those with higher noise exposure.
Materials and Their STC Ratings
Different building materials have varying STC ratings, which affect their use in soundproofing during construction projects.
Common Flooring Materials
Common flooring materials, including hardwood, laminate, and carpet, each possess unique STC ratings that affect their sound transmission properties.
Hardwood usually has an STC rating near 30, so it doesn’t block sound as well as carpet, which can have STC ratings of 50 or more. Laminate falls in the middle, averaging an STC of about 35.
To make sound absorption better, think about underlayment choices like cork, which can increase STC ratings by as much as 10 points, or foam underlayment that offers a budget-friendly option without losing effectiveness.
Installing these underlayments can significantly reduce noise, especially in multi-story buildings.
Comparison of STC Ratings by Material
A comparative analysis of STC ratings across various materials reveals significant differences that can guide soundproofing efforts.
For example, drywall usually has an STC rating between 30 and 36, which makes it suitable for a lot of uses. In contrast, concrete boasts a much higher rating of 50-55, offering superior sound insulation, but at a greater cost and weight.
Plywood falls in the middle with an STC rating of 32-36; it can be useful where lighter materials are desired.
When selecting materials, consider the specific soundproofing needs and constraints of your project, balancing performance with installation and budget factors for the best results.
Impact of STC on Building Design

STC ratings greatly affect building design, guiding choices on materials and layouts to improve sound insulation and privacy.
Regulatory Standards and Building Codes
Compliance with regulatory standards and building codes, including STC requirements, is essential for successful construction projects.
To improve soundproofing and meet STC requirements, consider using strategies like installing double stud walls, which reduce sound traveling between rooms.
Installing sound-dampening insulation materials, such as Rockwool or acoustic batts, can significantly improve sound attenuation.
For flooring, opt for resilient materials like cork or rubber, which absorb sound more effectively than traditional hardwood.
Always check local building rules and look at resources like the International Building Code (IBC) to follow regulations.
This combination improves comfort and helps with project quality and market appeal.
Acoustic Considerations in Residential vs. Commercial Spaces
Different sound issues come up in homes compared to business places, requiring specific methods for soundproofing.
In homes, materials such as fiberglass insulation, acoustic panels, and resilient channels are important for reducing noise between rooms and from outside.
For instance, using dense fiberglass batts within walls can significantly reduce sound transmission. On the other hand, commercial spaces often gain from using materials that absorb sound like acoustic ceiling tiles and carpets that reduce noise. These materials improve sound quality and make the work area more comfortable.
Therefore, assessing each space’s purpose will guide the selection of the most appropriate materials for effective sound insulation.
Enhancing STC Ratings in Flooring
Using different techniques can greatly improve the STC ratings of flooring, helping to reduce noise in various settings.
Soundproofing Techniques
Different soundproofing methods, like separating structures and increasing weight, can successfully improve the STC ratings of flooring systems.
For example, putting Green Glue Compound between layers of drywall or flooring improves sound isolation by cutting down vibrations. It can make STC ratings go up by as much as 10 points.
Similarly, installing acoustic backer panels can create a barrier that absorbs sound, further reducing transmission. Using mass-loaded vinyl (MLV) makes floors heavier and thicker, which helps to block noise.
Using these methods together reduces sound effectively and customizes solutions for particular acoustic requirements.
Choosing the Right Underlayment
Selecting the appropriate underlayment is critical for improving STC ratings in flooring applications, particularly in multi-family structures.
Different types of underlayment serve various flooring materials and performance needs. For instance, foam underlayment is ideal for laminate or engineered wood floors due to its sound absorption and moisture resistance, generally providing STC ratings between 20-25.
Conversely, cork underlayment offers a natural barrier for hardwood floors with an STC rating of 25-30, enhancing comfort and insulation.
When selecting, consider the flooring type and the specific sound transmission concerns of your space, ensuring the chosen underlayment aligns with your goals for noise reduction and comfort.
Case Studies
Looking at real-world examples shows practical soundproofing methods that effectively solved STC-related problems in different environments.
Residential Flooring Solutions
In residential projects, effective soundproofing solutions like floating floors and specialized underlayments have significantly improved STC ratings.
For instance, a recent case in a multi-unit apartment saw a 20% reduction in noise complaints after installing a floating floor system combined with a high-density underlayment. This setup achieved an STC rating improvement from 50 to 55, satisfying tenant expectations.
Tools like acoustic caulking and soundproofing panels can improve results, especially in shared walls. Homeowners should consider consulting with specialists to tailor solutions to their specific environmental conditions, ensuring the best soundproofing outcomes.
Commercial Flooring Applications
Commercial spaces need strong soundproofing methods, often using high-tech materials to meet strict STC standards.
For example, a top-level recording studio might use mass-loaded vinyl (MLV) with a 26 STC rating to reduce outside noise.
Acoustic panels made from fiberglass can absorb sound within the space, enhancing audio clarity and comfort.
An office building might use resilient channel systems in drywall installations to decouple walls and prevent sound transmission, achieving an STC rating of 50 or higher.
Choosing the best material is important; finding the right mix of price and effectiveness results in the best soundproofing.
Future Trends in STC Ratings
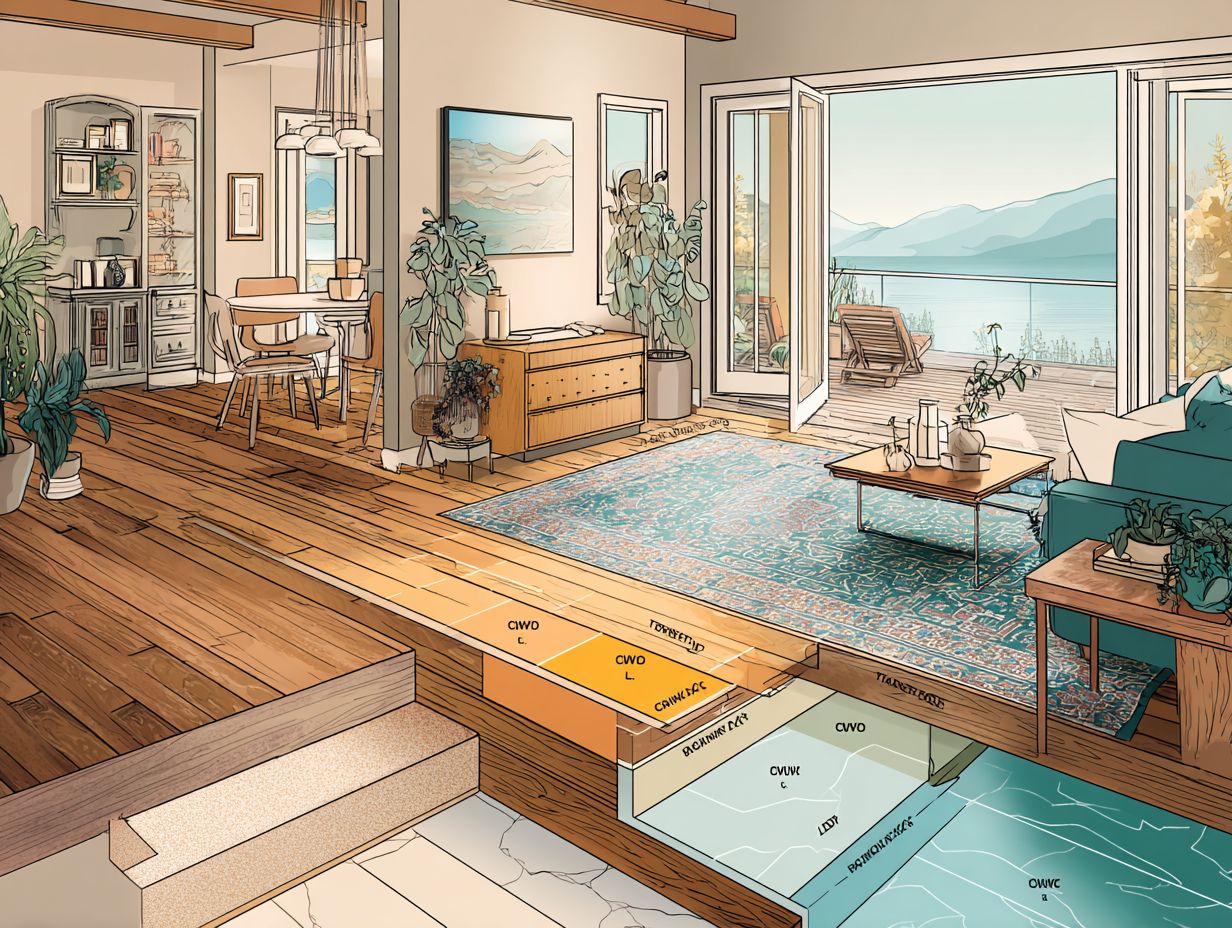
New developments in STC ratings show an increasing attention to using environmentally friendly and innovative methods for soundproofing materials and techniques.
Innovations in Flooring Materials
Recent advancements in flooring materials, like environmentally friendly composites, are leading to better sound transmission class (STC) performance and sustainability.
For instance, products like HempWood and bamboo flooring provide exceptional sound transmission class (STC) ratings, often exceeding 50, while being biodegradable.
Companies are introducing acoustic underlayment choices made from recycled materials that improve soundproofing. Brands like Floor Mates and QuietWalk offer underlayment solutions that integrate easily with various flooring types, ensuring reduced sound impact.
As buyers pay more attention to sustainability, these developments improve sound comfort and support environmental values, leading to a market focused on eco-friendly home improvements.
Predictions for STC Standards
Predictions indicate that STC standards will evolve, driven by increasing awareness of noise reduction’s importance in urban environments.
Experts expect that upcoming changes will involve tighter rules on building materials and construction methods to improve sound insulation.
For instance, the incorporation of advanced acoustic panels and soundproof windows is likely to become a standard requirement.
Industry reports suggest that city planners might use improved zoning laws to control noise in neighborhoods, creating a quieter place to live.
Keeping up-to-date with organizations like the National Institute of Building Sciences helps builders and developers follow regulations and stay competitive as things change.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Sound Transmission Class (STC) rating for flooring?
The Sound Transmission Class (STC) rating for flooring is a measure of how well a floor or floor covering blocks sound transmission from one space to another. It is typically used to assess the effectiveness of flooring in reducing noise from floor to floor.
How is the STC rating determined for flooring?
The STC rating for flooring is found by doing a sound transmission test in a lab. The test measures the sound transmission loss of the flooring material and assigns it a numerical rating on a scale from 25 to 90. The higher the rating, the better the flooring is at blocking sound.
What factors can affect the STC rating of flooring?
The type and thickness of the flooring material, as well as the construction of the subfloor and the presence of any additional soundproofing materials, can all affect the STC rating of flooring. The rating may also be influenced by the type and volume of noise being transmitted.
What STC rating is considered to be good for flooring?
A good STC rating for flooring is generally considered to be above 50. This means that the flooring is effective in blocking most common noises, such as conversation and television, from transferring from one space to another. Higher ratings, above 60, are even better at reducing noise transmission.
Can flooring with a high STC rating completely eliminate noise from transferring between spaces?
No, even flooring with a high STC rating cannot completely eliminate noise transmission. It can significantly reduce noise, but some low-frequency noises and vibrations may still be able to pass through. Other factors, such as gaps or cracks in the flooring, can also affect the effectiveness of the STC rating.
Is the STC rating the only factor to consider when choosing flooring for noise reduction?
No, the STC rating is not the only factor to consider when choosing flooring for noise reduction. Other factors, such as the use of additional soundproofing materials and proper installation, also play a significant role in reducing noise. It is important to consider all of these factors when selecting flooring for a specific space.



